Structure of DNA:
In 1953. James Watson and Francis Crick proposed DNA structure based on X-ray crystallographic studies provided by Maurice Wilkins and Rosalind Franklin.
I. DNA molecule as a double helix:
- DNA molecule consists of two long strands.
- The strands are coiled around a common, imaginary central axis to form a double helix.
- It looks like a twisted ladder
II Structure of each strand:
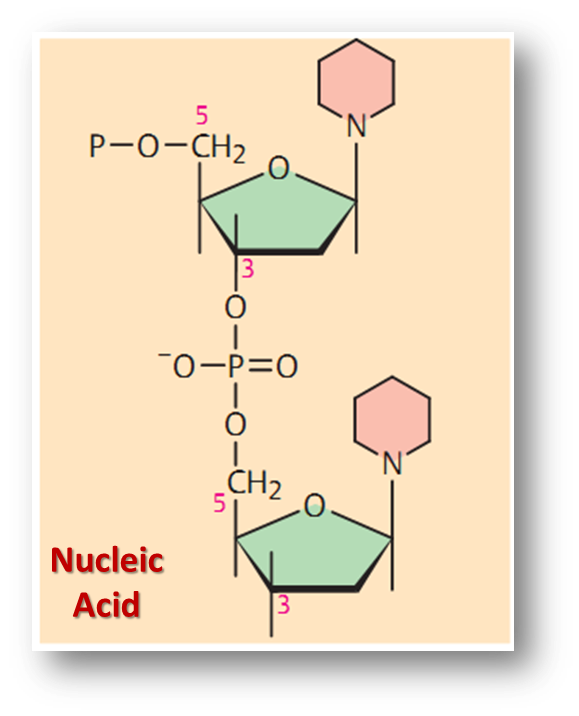
- Each strand of DNA consists of number of nucleotides.
- Each nucleotide is made up of deoxyribose sugar, phosphate group and a nitrogen base.
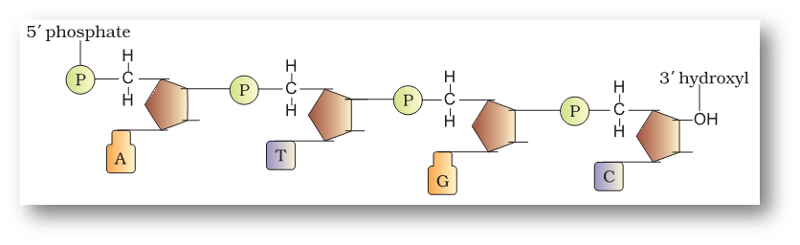
- The successive nucleotides of the same strand are linked by 3' - 5'. phosphodiester linkages.
- Phosphate attached to 5th carbon, of a sugar of nucleotide is joined to 3rd carbon of another.
III. Complementary base pairing:
The nitrogen bases present on one strand, pair with the nitrogen bases of opposite strand.
The pairing of Purine and Pyrimidine bases is termed as complementary base pairing.
Purines : Pyrimidines
Adenine = Thymine (A=T or T=A)
Guanine = Cylosine (GΞC or CΞG)
The sequence present on one strand of DNA decides the base sequence of the other strand.
The nitrogen bases along with hydrogen bonds make up the rungs of the ladder. These are also referred to as transverse bars.
The distance between two successive steps or rungs is 0.34 nm.
IV Purine: Pyrimidine ratio [Chargaff's Rule]
Due to complementary base pairing, total number of purine bases is always equal to the total number of pyrimidine bases (1:1 ratio).
This is called Chargaffs rule. It may be represented as

 and
and 

V Polarity of strands:
- One end is considered as 5' end whereas the other end is 3' end .
- This polarity is because of 3rd and 5th carbon atoms of the deoxyribose sugar. At 5' end there is a free phosphate group while at the 3' end there is a free -OH group.
- One of the strands runs in 5' ―› 3' direction while the other in 3' ―› 5' direction.
- DNA strand is anti parallel. Hence, the 5' end of one strand lies close to the 3' end of the other strand and vice versa.
VI Major and minor grooves:
- Normally the strands of DNA undergo right-handed coiling around a central imaginary axis.
- The coiling of the double helix results in formation of major or deep grooves.
- The twisting of two strands around one another forms the minor or shallow grooves.
- They are found in alternate manner.
VII Dimensions:
The diameter of DNA molecule is 2 nm.
The spiral ladder like arrangement of DNA molecule is due to deflection angle of 36° between two successive steps (rungs).
DNA molecule makes one complete 360° turn after covering a distance of 3.4 nm (0.34 nm x 10 steps = 3.4 nm).
There are 10 base pairs in one complete spiral.(1 nm = 10 A°).
