Packaging of DNA
Length of DNA double helix molecule, in a typical mammalian cell is approximately 2.2 meters.
Approximate size of a typical nucleus is I0"6m.
DNA is therefore must be condensed and coiled and super coiled to fit in the nucleus.
In Eukaryotes. this packaging or organization of DNA is complex.
- Histones are required for the packaging of DNA.
- Histones are proteins that are rich in the basic amino acid residues lysines and arginines which carry positive charge in their side chains.
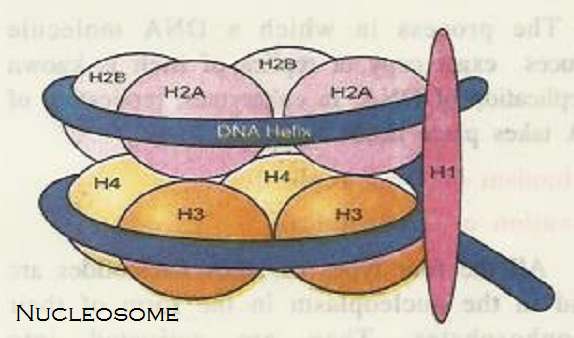
- Eight molecules of histones (two each of H2A, H2B, H3 and H4) get organized to form histone octamer.
- DNA is negatively charged and it is wrapped around the positively charged histone octamer to form nucleosome.
Under the electron microscope,
- nucleus shows chromatin network.
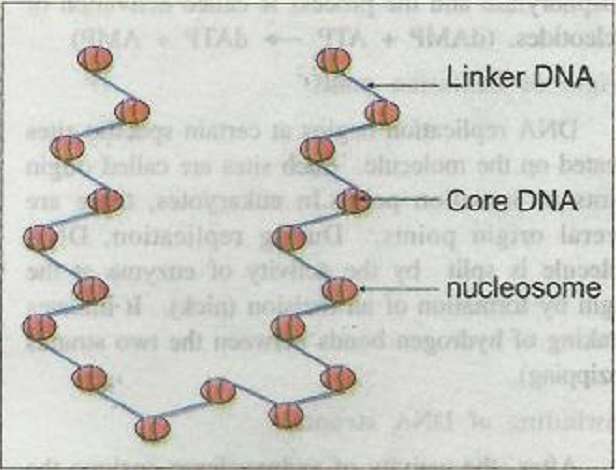
- The nucleosomes in chromatin are seen as *beads-on- string'.
- Around the octamer, DNA molecule is wrapped as 1 and 3/4th turn.
- This DNA is called core DNA and it consists of about 146 bp (base pairs).
- Adjacent nucleosomes are linked with small segments of DNA called linker DNA
- It has about 54 bp.
- Thus the string is DNA- 2nm or 20A in diameter.
- This 'beads- on- string' structure gets condensed into nucleosome fiber, which is 10 nm (100A) in diameter.
- H1 histone is present in the linker region.
- DNA makes two complete turns wrapping the octamer and leaves it.
- Each nucleosome contains 200 bp of DNA helix.
- The thin and long nucleosome fiber is coiled like a telephone wire to make solenoid fiber with diameter 30 nm or 300A.
- Nucleosome and solenoid fibers are characteristic of nucleus at interphase.
- During prophase of cell division,
- there is formation of chromatin fibers of 200 nm
- and then a chromatid of 700nm.
- At metaphase of cell division
- a chromosome with two chromatids joined by common centromere can be seen under the compound microscope.
- The packaging of chromatin at higher levels need additional set of proteins that are collectively called Non-Histone Chromosomal (NHC) proteins.
- Loosely packed region of chromatin that stains light is called Euchromatin
- Densely packed region that stains dark is called Heterochromatin.
- Euchromatin is considered as transcriptionally active chromatin, while heterochromatin is inactive.
