Types of inflorescence :
a. Racemose :
Growth of peduncle is infinite or unlimited.
Apical bud is free for continuous growth.
Flowers are borne in acropetal succession.
(Mature flowers at the base) Order of opening is centripetal.
b. Cymose:
Growth of peduncle is finite limited.
Apical meristem terminates into flower.
Flowers are borne in basipetal succession.
(Mature flowers at the apex) Order of opening is centrifugal.
Flower :
Flower is highly modified and condensed shoot meant for sexual reproduction.
On the basis of position a flower can be axillary or terminal.
In a typical flower, the thalamus.
Thalamus consists of four compactly arranged nodes and three highly condenseed internodes.
From each node of thalamus, a circle or whorl of modified leaves is produced.
A flower may or may not show presence of bract at base of pedicel or over the pedicel, such a flower is said to be bracteate or ebracteate respectively.
A flower with pedicel is said to be pedicellate flower and without pedicel is called as sessile flower.
Flower with bilateral symmetry or Clitoria is called zygomorphic flower e.g. Sweet pea
Flower with radial symmetry is called actinomorphic flower e.g. Sunflower.
Terminologies related to flower :
1. Complete : Presence of all four floral whorls.
2. Incomplete : Absence of any one of the floral whorl.
3. Perfect : Both androecium and gynoecium are present, also called as hermophrodite or bisexual flower.
4. Imperfect : Any one reproductive whorl is present also called as monophrodite or unisexual flower.
5. Unisexual : It can be either staminate (male)/ pistillate (female) flower
6. Neuter : When both reproductive whorls are absent, it is said to be neuter flower e.g. Ray floreti of sunflower.
7. Monoecious plant : Male and female reproductive flowers are borne on same plant. E.g. Maize.
8. Dioecious plant : Only one type of unisexual flowers are present on plant e.g. Date palm.
Insertion of floral whorls:
The position and arrangement of rest of the floral whorls with respect to gynoecium on the thalamus is known as insertion of floral whorls.
In a typical flower thalamus consist of four compactly arranged nodes and three internodes.
Slope of thalamus decides insertion of floral whorls.
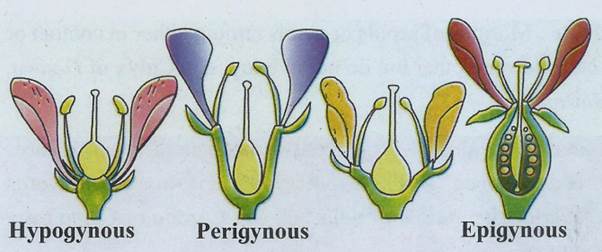
a. Hypogyny :
When the convex or conical thalamus is present in flower, ovary occupies the highest position while other floral parts are below ovary.
Ovary is said to be superior and flower is called as hypogynous flower.
E.g. Brinjal, Mustard, China rose etc.
It is denoted as G in floral formula.
b. Perigyny :
When cup shaped or saucer shaped thalamus is present in a flower, ovary and other floral parts occupy about same position, Such an ovary is said to be semi- superior or semi-inferior.
All floral whorls are at the rim of thalamus. Flower is perigynous e.g. Rose, Pea, Bean, etc. It is denoted as G- in floral formula.
c. Epigyny :
When thalamus completely encloses ovary and may show fusion with wall;
the other floral parts occupy superior position and ovary becomes inferior. Such flower is said to be epigynous flower, e.g. Sunflower, Guava etc. It is denoted as G in floral formula.
