Fruit :
Angiosperms produce fruit after fertilization from ovary.
Sometimes fruit is produced from ovary without fertilization. Such types of fruits are called as parthenocarpic fruits and phenomenon is called as parthenocarpy. E.g Banana, Grapes, etc. without or with one or more seeds.
The fruit which develops only from ovary is true fruit or eucarp. e.g. Mango.
The fruit which develops from ovary and any other floral part is false fruit of pseudocarp. e.g. Apple.
True fruit has a wall (pericarp) and seeds.
Pericarp is further divided in
- outer epicarp,
- middle mesocarp and
- inner endocarp.
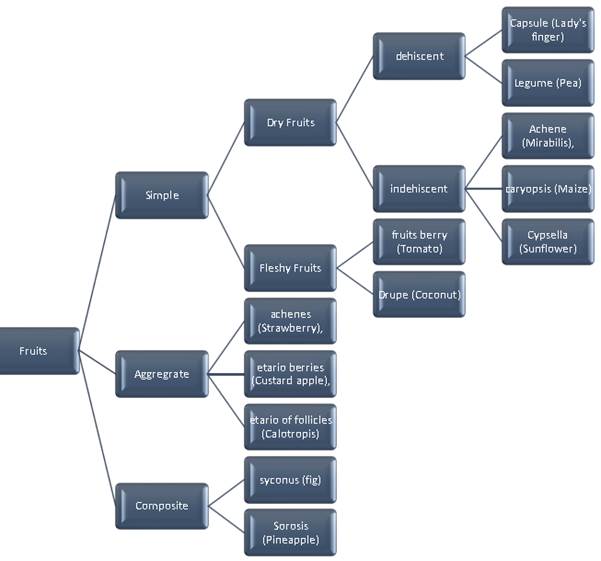
Fruits can develop from one ovary of one flower. Such fruits are simple fruits.
Simple fruits are further classified on the basis of their pericarp.
Those having thin pericarp are dry fruits but those with thick pericarp are fleshy fruits.
In dry fruits, the pericarp becomes dry and thin. It breaks open (dehiscent) at maturity.
But in some others it does not break open (indehiscent). Achene (Mirabilis), caryopsis (Maize) and Cypsella (Sunflower) are indehiscent fruits.
Capsule (Lady's finger) and legume (Pea) are dehiscent fruits.
In fleshy fruits berry (Tomato) has a very soft pericarp but drupe (Coconut) has stony endocarp.
Many ovaries of apocarpous gynoecium can form one fruit. Such fruits are aggregate fruits.
Aggregate fruits are a collection (Etario) of many varieties. Accordingly they can be etario of achenes (Strawberry), etario berries (Custard apple), etario of follicles (Calotropis), etc.
Many ovaries of many flowers but of one inflorescence can form one fruit. Such fruits are composite fruits. These fruits develop from one inflorescence.
The one which develops from hypanthodium inflorescence is syconus (fig).
Sorosis (Pineapple) develops from Catkin inflorescence.