Classification of Meristems:
The meristematic tissues are confined to some parts of plant body.
These are called growing regions or meristems.
Meristems may be classified on the basis of following criteria.
A) Origin and development
B) Position in plant body
C) Functions
A) Meristems based on Origin and Development:
On the basis of origin and development, the meristematic tissues are classified into the following three groups:
1. Promeristem or primordial meristem:
It is a group of cells representing primary stage of meristematic tissue.
It is the initial meristem and occupies a small area at the tip of the stem and the root.
It occurs in embryonic stage of plants.
By repeated cell division the promeristem gives rise to primary meristem.
2. Primary meristem:
The meristems which originate from promeristem are called primary meristems.
They exist in the plant body right from the beginning.
These cells are always in active state of division and give rise to primary permanent tissues.
They form the basic structure of plant body.
They are present at the apices of shoot and root.
3. Secondary meristem:
The meristems which develop in a plant body during the later stages of growth are called secondary meristems.
They arise in primary permanent tissues (parenchyma).
It give rise to the secondary permanent tissue which adds to the girth of the plant.
The cambium of root, interfascicular cambium of stem and cork cambium in both root and stem are examples of secondary meristems.
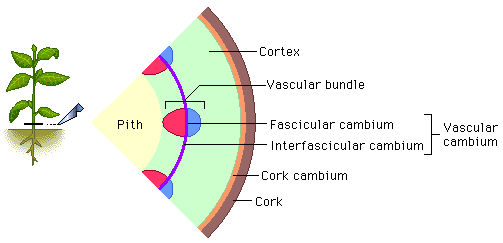
They arise from parenchyma by de-differentiation, i.e. parenchyma re-gains the capacity to divide.
