B) Complex Permanent Tissue:
A complex tissue is made up of different types of cells.
Vascular tissues of plants (Xylem and Phloem) are complex tissues.
A complex tissue can be defined as a group of different types of cells that perform a common function.
All the cells of a complex tissue work as a single unit.
Complex tissue is a heterogeneous tissue.
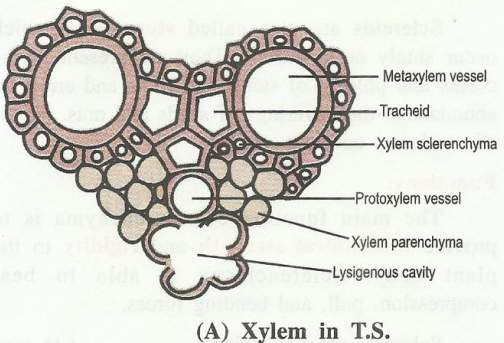
1. Xylem (Wood):
It is a complex permanent plant tissue, which performs the function of
transport of water and minerals (inorganic sap), upwards from roots to the leaves.
In addition, it provides mechanical strength to the plant body.
Xylem is also known as wood.
It is made of four types of cells.
i) Tracheids,
ii) Vessels (Tracheae),
iii) Xylem fibres,
iv) Xylem Parenchyma
i) Tracheids:
Tracheids are elongated, tubular cells with tapering ends and are dead at maturity.
The cell wall is thick due to deposition of lignin.
The tracheids possess various kinds of thickenings, such as;
- annular (in the form of rings),
- spiral (in the form of spring or helix),
- reticulate (in the form of a network),
- scalariform (a ladder-like), or pitted.
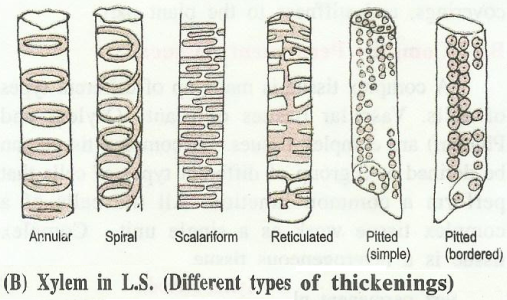
Pitted is the most advanced type of thickening.
Tracheids are uniformly thickened except for small circular areas called pits, which may be simple or bordered.
Tracheids form main water conducting elements of xylem in Pteridophyta and Gymnosperms.
Few tracheids occur in xylem of Angiosperms also.
ii) Vessels (Tracheae):
The vessels are elongated, tube-like structures.
Many vessel elements are placed end to end in longitudinal series.
Their transverse walls are dissolved or perforated (with many pores).
The walls of vessels are
- lignified,
- relatively less thick
- the coil cavity or the lumen is wider (as compared with tracheids).
The lignified walls show different patterns of thickening like tracheids.
The first formed xylem vessels (protoxylem) are small and have either annular or spiral thickening.
The larger vessels, metaxylem, have reticulate or pitted thickening.
Presence of vessels is a characteristic feature of Angiosperms.
Vessels are absent in Pteridophytes and most Gymnosperms.
iii) Xylem fibres:
Sclerenchymatous cells found in xylem are called wood fibres.
They are elongated, narrow and spindle-shaped cells tapering at both the ends.
The walls are lignified.
They provide mechanical support to the plant body.
iv) Xylem (wood) parenchyma:
These are parenchymatous cells present in the xylem in association with tracheids and vessels.
They help m the lateral conduction of water and mineral elements, and also store food material.
