Skip to main content
SITE OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS: Chloroplast
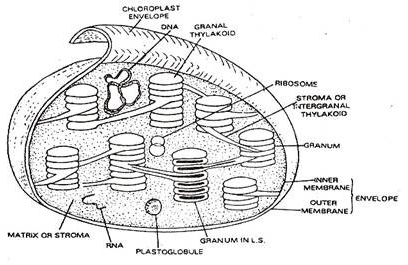
- Chloroplast is a double membrane bound structure and an outer and inner membrane is collectively called Peristromium.
- It encloses colorless, colloidal matrix called Stroma.
- It contains enzymes for reduction of CO2 into glucose (dark reaction), 70S ribosomes and DNA.
- DNA is Circular, closed, naked ring and is called plastidome.
- Since the DNA is present, the Chloroplast is self-replicating and semi-autonomous cell organelle.
- Embeded in the stroma, there are approximately 40 to 60 green colored structures called Grana.
- Each granum consists of small, disc-like lamellae or Thylakoids.
- The Photosynthetic pigments are embed in the Thylakoids.
- ATP synthesis (light reactions) takes place in grana.
- Grana are interconnected by membranes called stroma lamellae or inter granal or fret membranes,
- The stroma lamella helps in rapid transport of materials.
- In prokaryotes, chloroplasts are absent and pigments are located in lamellae i.e. (Thylakoid).
- According to Park and Biggins, photosynthetic pigments are located in the membranes of Thylakoids in specific areas called Quantasomes.
- A quantasome is a photosynthetic unit. Later on. Emerson established the presence of two distinct groups, PS-I and PS-II.


