DEVIATION FROM MENDELIAN RATIO/POST MENDELIAN GENETICS/ NEO-MENDELIAN GENETICS
What are the two types of gene interaction ? Give their examples.
i) There are two types of gene interactions, viz,. intragenic or intrallelic and intergenic or interallelic.
ii) The intragenic interactions occur between the alleles of the same gene. Incomplete dominance, codominance, multiple alleles, etc. are the examples of intragenic inheritance.
iii) Intergenic interactions occur between the alleles of different genes.
iv) Pleiotropy, polygenes, epistasis, supplementary and complementary genes are the examples of intergenic interactions.
What are the different types of Gene Interaction ?
i) Intragenic (interallelic) occur between alleles of same gene e.g. incomplete dominance, co-dominance and multiple alleles.
ii) Intergenic (nonallelic) occur between the alleles of different genes on the same or different chromosome such as pleiotropy, polygenes, epistasis, supplementary and complementary genes, etc.
Explain incomplete dominance with example.
OR
Explain deviation of mendel with example of Mirabilis jalapa /4 O'clock plant.
In incomplete dominance both the genes of an allelomorphic pair express themselves partially.
One gene cannot suppress the expression of the other completely. Thus the pair is not as one dominant and other recessive.
In such cases there is intermediate expression in F1 hybrids.
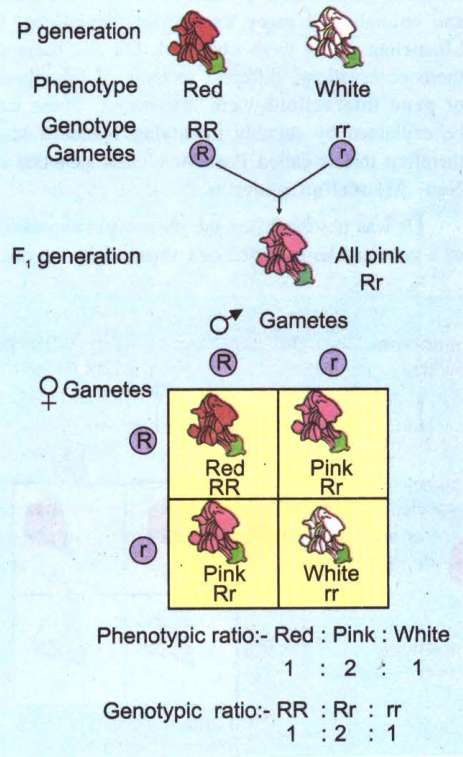
In _four o' clock plant, (Mirabilis jalapa), there are two pure varieties; when one with red (RR) flowers is crossed with other with white (rr) flowers.
The F I hybrids bear pink (Rr) flowers.
When by selfing of F1 hybrids, F2 generation was raised, it showed; red (RR), pink (Rr) and white (rr) in 1:2:1 ratio. (Phenotypic and genotypic ratio is same.)
This means factors segregate and there is no mixing of the factors.
The intermediate shade is produced due to incomplete dominance.
Incomplete dominance does not favour the blending theory of inheritance, though in F1 all are pink; both the parental traits, red and white reappear, each in 25%, in F2 generation.
Other similar example is Snapdragon, (Antirrhinum majus).
Explain co-dominance with suitable example.
In co-dominance, both the genes of an allelomorphic pair express themselves equally in F1 hybrids.
Such alleles which are able to express themselves independently even if present together in hybrids are called codominant alleles.
Thus, in co-dominance both alleles are expressed.
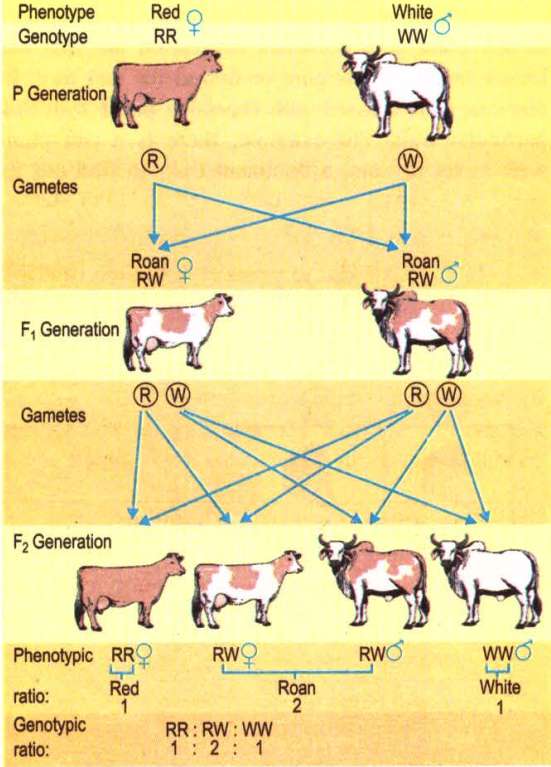
Roan coat colour in Cattle.
i) There are two types, one with red coat (skin with red colour hair) and the other with white coat (with white hair).
ii) When red cattle (RR) are crossed with white cattle (WW), F1 hybrids (RW) have roan colour. Roans have the mixture of red and white colour hair.
iii) Thus both the traits are expressed equally. In F2 generation (produced by interbreeding of roans) red (RR), roans (RW) and white (WW) are produced in the ratio 1 : 2 : 1.
iv) Thus in co-dominance also genotypic and phenotypic ratios are identical.
Blood group 'AB' in human is also an example of co-dominance as well as Multiple allele.
i) Blood group character is controlled by gene I, that exists in three allelic forms IA, IB and IO.
ii) In IA and IB,superscripts A and B stand for glycoproteins(sugar polymers) that are found projecting from the surface of RBCs.
iii) The allele IA produces glycoprotein A while IB produces glycoprotein B,allele IO does not produce any of them.
iv) The allele IA is dominant over IO. IB is also dominant over IO.
v) Allele IA and IB are co-dominant and express themselves when present together, hence RBCs have both the types of glycoprotein and blood group will be AB.
What is multiple allelism ? Explain with the example.
More than two alternative forms (alleles) of a gene in a population occupying the same locus on a chromosome or its homologue are known as multiple alleles.
Multiple alleles arise by mutations of the wild type of gene.
A gene can mutate several times producing a series of alternative expressions.
Different alleles in a series show dominant - recessive relation or may show co-dominance or incomplete dominance among themselves.
An individual is with any two alleles of a gene, one on each chromosome of the homologous pair.
Wild type is dominant over all other mutant alleles.
Multiple alleles do not undergo crossing over.
Example Drosophila - Wing type
The series of wing abnormality ranging in size from normal wings to no wings.
The normal wings is wild type and is denoted by Vg +.
The extreme expression with no wings i.e. just stumps, is due to one allele vg, in homozygous condition.
Following table shows the complete series.
|
Phenotype |
Genotype |
|---|---|
|
Normal Wings |
Vg+ |
|
Nicked Wing |
vgni |
|
Notched Wing |
vgno |
|
Strap Wings |
vgst |
|
Vestigeal wings |
vg |
ABO blood groups in human beings.
The gene I controls the ABO blood groups.
It has three allele; IA, IB and i.
The allele IA and 18 produce a slightly different form of the antigen and allele i, does not produce any antigen.
Since humans are diploid organisms, each person possesses any two of the three I gene alleles.
IA and IBare co-dominants and are completely dominant over i.
There are six different genotypes and only four different phenotypes, i.e. blood groups as follows:
|
Genotype |
Phenotype |
|---|---|
|
IAIA or IAi |
A |
|
IBIB or IBi |
B |
|
IAIB |
AB |
|
ii |
O |
