5.3.3 Types of Vascular Bundles:
The vascular tissues occur in the form of distinct patches called the vascular bundles.
According to the arrangement of xylem and phloem, vascular bundles are classified in the following types.
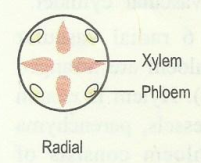
1.Radial vascular bundle:
The vascular bundles, in which xylem and phloem are arranged radially
- in the form of separate bundles on different radii, are called radial vascular bundles.
The xylem and phloem bundles are arranged alternating with each other.
Such vascular bundles are characteristic of roots.
2. Conjoint vascular bundle:
A vascular bundle in which xylem and phloem are present on same radius is called a conjoint vascular bundle.
Here xylem and phloem together form a bundle. Such vascular bundles are of the following two types:
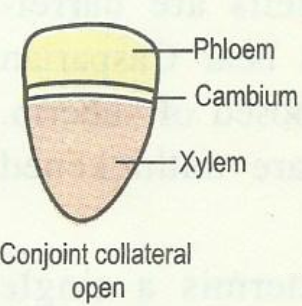
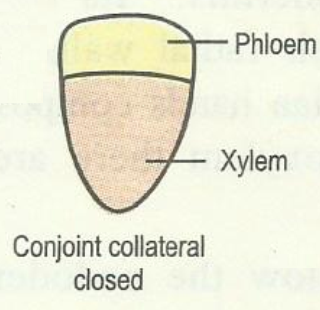
i) Collateral vascular bundle:
In this type of vascular bundle,
xylem and phloem are present on the same radius in such a way that xylem lies inwards and phloem outwards.
In dicot stems, cambium lies between xylem and phloem.
Such vascular bundles are called open (secondary growth present).
In monocot stems cambium is absent and such vascular bundles are called closed (secondary growth absent).
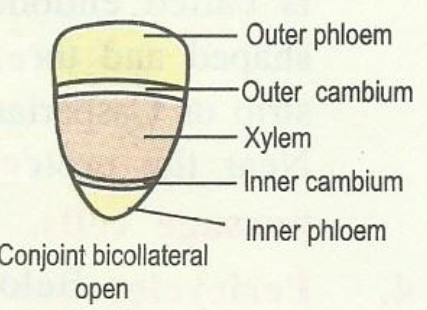
ii) Bicollateral vascular bundles:
The vascular bundle in which phloem occurs in two groups inside and outside the xylem, is called a bicollateral vascular bundle.
In such vascular bundles there are two strips of cambium one on either sides of xylem.
Vascular elements are arranged in the following sequence
- outer phloem,
- outer cambium,
- xylem,
- inner cambium
- inner phloem.
Such vascular bundles are commonly found in the members of family Cucurbitaceae.
They are always open.
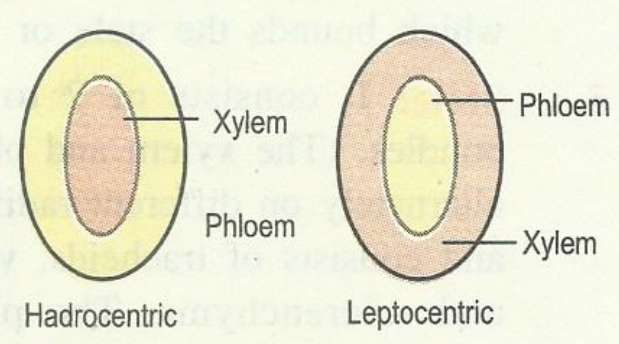
3. Concentric vascular bundles:
The conjoint vascular bundle,
in which one type of vascular tissue is surrounded by the other, is called concentric vascular bundle.
When xylem is surrounded by phloem, it is called hadrocentric
when phloem is in the centre, it is called leptocentric.
Concentric bundles are always closed.