C4 Plants [Dicarboxylic acid cycle]
In certain tropical plants, CO2 is not directly absorbed by RUBISCO.
Due to low concentration of CO2, they follow another pathway.
In this alternative pathway, the first stable compound is a 4-C compound, Oxalo Acetic acid.
Hence, it is called C4 palhway (or dicarboxylic acid cycle).
The plants like maize, sugarcane, jowar, Amaranthus etc. have this C4 pathway.
H.P. Kortshak reported this alternative method of CO2 fixation for the first time (in 1965) in sugarcane.
In 1970 M.D. Hatch and C.R. Slack outlined the entire series of reactions; hence it is called Hatch and Slack pathway or HSK pathway.
Kranz Anatomy: (Kranz - meaning wreath or necklace)
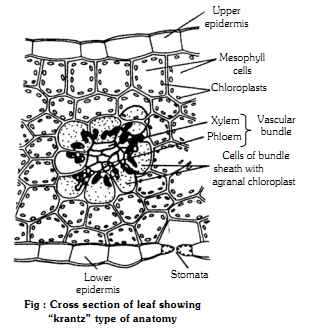
C4 plants show Kranz anatomy.
The mesophyll is not differentiated into palisade and spongy tissue.
It is homogenous.
Each vascular bundle is surrounded by a ring ot wreath of radially arranged large bundle sheath cells.
These cells contain agranal chloroplasls, i.e. chloroplasts are without grana.
The agranal chloroplasls are bigger in size, less in number and are with only stroma.
The chloroplasls in mesophyll cells contain granal chloroplasts. They are smaller in size, more in number, with abundant grana and very less stroma.
Thus chloroplasts show dimorphism in C-4 plants.
The enzyme, PEP carboxylase is present in mesophyll chloroplast.
The enzyme, RUDP or RUBP carboxylase (RUBISCO) is present in bundle sheath chloroplast.
Mechanism of HSK or C4 pathway
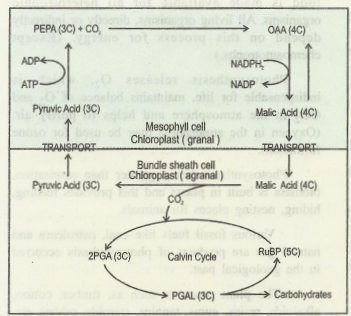
The reactions occurring in this pathway are completed in two parts and at two different sites.
- Part - I - (Reactions in Mesophyll cells)
- Part - ll- (Reactions in Bundle sheath cells)
Part - I- (Reactions in Mesophyll cells) - Carboxylation (First CO2 fixation)
Atmospheric CO2 entering through stomata is accepted by phosphoenol pyruvic acid (PEPA), a three carbon compound, present in the mesophyll cells.
In the presence of water and enzyme PEP carboxylase, PEPA gets carboxylated to form oxalo-acetic acid (OAA), a four-carbon compound.
The enzyme PEP carboxylase can function even if the concentration of CO, in atmosphere is as low as 2 ppm (parts per million).
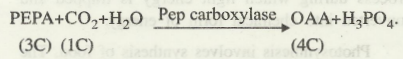
Part - I- (Reactions in Mesophyll cells) - Reduction
Oxalo-acetic acid is reduced to Malic acid in the presence of NADPH2 and an enzyme Malate dehydrogenase.
Or
OAA is changed to aspartic acid by amination in the presence of NADPH2 and an enzyme transaminase.

Part - ll- (Reactions in Bundle sheath cells) - Decarboxylation
Malic acid (or aspartic acid) is transported to chloroplasts of bundle sheath cells.
In these agranal chloroplasts, malic acid undergoes decarboxylation in the presence of NADP to form pyruvic acid and CO2 is released.
Hydrogen removed at this step forms NADPH2.
If aspartic acid is formed, it undergoes deamination to form pyruvic acid.

Part - II - (Reactions in Bundle Sheath cells) - Second CO2 fixation
The CO2, released is accepted by a second CO2 acceptor RUBP and is fixed by C3 pathway (Calvin cycle) in the agranal chloroplast of bundle sheath cells.
Thus, glucose is formed by Calvin cycle and is transported through phloem.
Pyruvic acid produced due to decarboxylation of malic acid.
Pyruvic acid is transported back to mesophyll cells and is phosphorylated by ATP to form PEPA.
PEPA, the initial acceptor is thus regenerated to continue the pathway.
Significance of C4 or HSK pathway
- In C4 plants CO2 fixation takes place twice, in two different cells during day.
- PEP carboxylase can pick up CO2 at very low concentration and C4 plants can photosynthesize in high light intensity, high temperature and less amount of water.
- Thus C-4 pathway has evolved in arid plants to maintain efficiency of photosynthesis under adverse conditions.
- In C4 plants PEP carboxylase (PEPCase) fixes CO2 at low CO2 concentration in the mesophyll cells.
- In the bundle sheath cells, CO2 concentration is more, so that RUBISCO functions as carboxylase and photorespiration is avoided.
- C-4 pathway is therefore also referred to as CO2 concentrating mechanism.
- Due to this some C4 plants, such as maize, sugarcane and jowar are more productive.
- In C4 plants light reaction takes place in mesophyll cells (granal chloroplasts) while dark reaction (Calvin cycle) in bundle sheath cells (agranal chloroplasts).
