Crassulacean Acid Metabolism
- In certain plants, (members of family Crassulaceae) like succulents and plants which grow in dry conditions, (xerophytes) stomata remain closed during day.
- It helps reduce the loss of water due to transpiration.
- Mechanism of photosynthesis in these plants is different and it is called Crassulacean acid metabolism. Such plants are called CAM plants.
- In these plants CO2 is taken up during night, when stomata are open, by PEPA and Oxaloacetic acid is formed in the presence of enzyme PEPcarboxylase.
- Oxalo acetic acid then gets reduced to malic acid in the presence of enzyme, malate dehydrogenase. Malate gets accumulated during night.
- During day, when stomata are closed, malate undergoes decarboxylation gradually and gets converted into pyruvate.
- CO2 thus released enters in Calvin cycle and sugar is produced, which subsequently gets converted into starch.
- Pyruvate also gets converted into starch. Thus starch gets accumulated during day.
- During night, from starch, PEPA is regenerated.
- Thus in CAM plants, C-4 pathway occurs during night and C-3 pathway during day. Acid concentration increases during night and decreases during day.
- This diurnal (day and night) fluctuation in acid concentration is characteristic feature of CAM plants, and Kranz anatomy is absent.
Interdependence of light and dark reaction
The two phases of photosynthesis, i.e. light and dark reactions are interdependent.
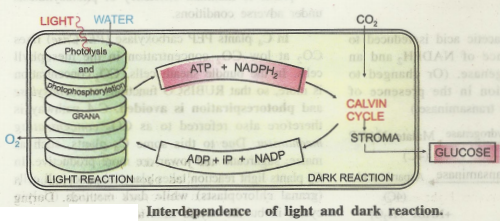
The products of light reaction, i.e. ATP & NADPH2 (assimilatory power) are required for dark reaction i.e. for reduction of CO2 into glucose.
During dark phase, ADP, iP, & NADP get regenerated, and are required for the synthesis of ATP & NADPH2, during light reaction.
Thus the two are interdependent. The dark reactions also take place during day.
