3.10 Sex Linked Inheritance :
Genes located on non-homologous region of sex chromosomes, are called sex-linked genes. The traits that are determined by sex linked genes, are called sex-linked traits.
The inheritance of sex linked genes from parents to their offsprings, is called sex linked inheritance.
There are two types of sex-linked genes as X-linked genes and Y-linked genes.
a. X-linked (sex linked) genes :
The X linked genes are located on non-homologous region of X chromosome and these gene do not have corresponding alleles on Y chromosome. Female has two X chromosomes. In female two recessive sex linked genes are required for expression of sex linked traits. If one X chromosome carries a recessive gene for sex linked trait (defect) its effect is suppressed by the dominant gene present on other X chromosome. The females with one recessive gene are carriers. The carrier female is physically normal as she does not suffer from the disease (disorder). Male has only one X-chromosome. If X chromosome carries X-linked recessive gene for sex linked trait, then it is expressed phenotypically, because there is no dominant gene on Y chromosome to suppress its effect. Therefore, sex-linked / X-linked traits appear more frequently in males than in the females. Examples of X-linked traits include haemophilia, colour blindness, night blindness, myopia, muscular dystrophy, etc.
b. Y-linked (Holandric) genes :
Genes located on non-homologous region of Y chromosome, are called Y linked genes. The Y-linked genes are inherited directly from male to male. In man, the Y-linked genes such as hypertrichosis is responsible for excessive development of hair on pinna of ear. This character is transmitted directly from father to son.
Colour blindness :
Colour blindness is X-linked recessive disorder where person is unable to distinguish between red and green colours as both the colours appear grey. It is caused due to recessive X-linked genes (XC) which prevents formation of colour sensitive cells, the cones, in the retina of eye. The homozygous recessive females (Xc Xc) and hemizygous recessive male (XcY) are unable to distinguish between red and green colours. The frequency of colour blind women is much less than colour blind men. Dominant X linked gene (XC) is necessary for formation of colour sensitive cells in the retina of eye. Thus, genotypes of male and female individuals can be represented follows:
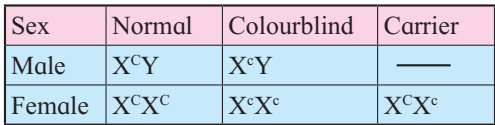
The inheritance of colourblindness can be studied in the following two types of marriages:-
1. Marriage between colour blind male with normal female, will produce normal visioned male and female offspring in F1. The sons have normal vision but daughter will be carrier for the disease.
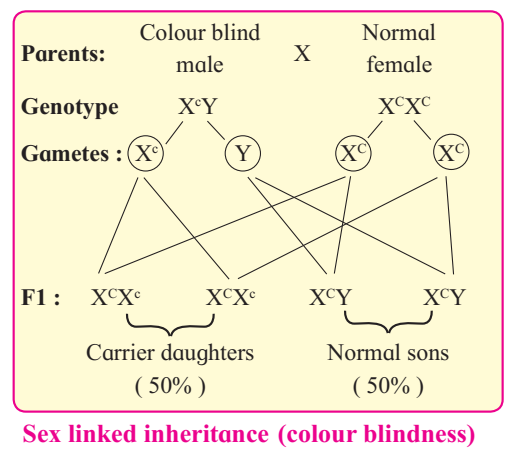
2. Marriage between carrier female (daughter) and normal male will produce female offsprings with normal vision but half of them will be carriers for the disease. Half of male offsprings will be normal while remaining half will be colour blind.
From above example, it is clear that the X linked recessive gene for colour blindness is inherited from colourblind father to his grandson through his daughter. This type of inheritance is called as cris-cross inheritance.
Haemophilia (Bleeder's disease) :
Haemophilia is X-linked recessive disorder in which blood fails to clot or coagulates very slowly.
The genes for normal clotting are dominant over the recessive genes for haemophilia.
The person having recessive gene for haemophilia is deficient in clotting factors (VIII or IX) in blood. Even minor injuries cause continuous bleeding, hence haemophilia is also called as bleeder's disease.
The recessive gene for haemophilia is located on non homologous region of X chromosome. As there is no corresponding allele on Y chromosome to suppress its expression, so men suffer from this disease. Women suffers only when both X chromosomes have recessive genes (alleles).
The genotype of male and female individuals can be represented as follow

Like colour blindness, haemophilia also shows criss-cross inheritance. The inheritance of haemophilia can be studied with the help of following examples -
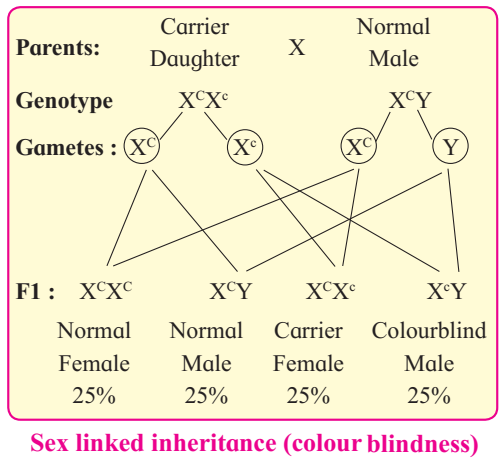
1. Marriage between the Haemophilic male and normal female.
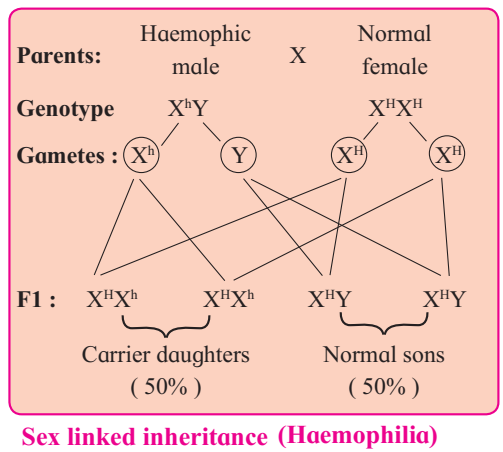
2. Marriage between carrier female (daughter) and normal male.

