3.12 Genetic Disorders :
Genetic Disorders are broadly grouped into two categories as, Mendelian disorders and chromosomal disorders,
Mendelian disorders are mainly caused due to alteration or mutation in the gene.
e.g. thalassemia, sickle cell anaemia, colourblindness, haemophilia, phenylketonuria, etc.
On the other hand, chromosomal disorders are caused due to absence or excess of one or more chromosomes or their abnormal arrangement.
eg, Down's syndrome, Turner's syndrome, Klinefelter's syndrome etc.
Thalassemia :
Thalassemia is an autosomal, inherited recessive disease. Haemoglobin molecule is made of four polypeptide chains- 2 alpha (a) and 2 beta (b) chains. The synthesis of alpha chains are controlled by two closely linked genes (HBA1 and HBA2) on chromosome 16 while the synthesis of beta chain is controlled by a single gene (HBB) on chromosome 11.
Depending upon which chain of haemoglobin is affected, thalassemia is classified as alpha-thalassemia and beta thalassemia. It is caused due to deletion or mutation of gene which codes for alpha (a) and beta (b) globin chains that result in abnormal synthesis of haemoglobin.
In Thalassemia, person shows symptoms like anaemia, pale yellow skin, change in size and shape of RBCs, slow growth and development, dark urine, etc.
Massive blood transfusion is needed to these patients. Thalassemia differs from sickle-cell anaemia. The former is a qualitative problem of synthesizing few globin molecule, while the latter is a qualitative problem of synthesizing an incorrectly functional globin.
Down's Syndrome (21st trisomy) :
Down's syndrome is named after the physician John Langdon Down who first described this autosomal chromosomal disorder in 1866.
This Syndrome is caused due to an extra copy of chromosome number 21st. It shows presence of three copies of 21st chromosome instead of homologous pair.
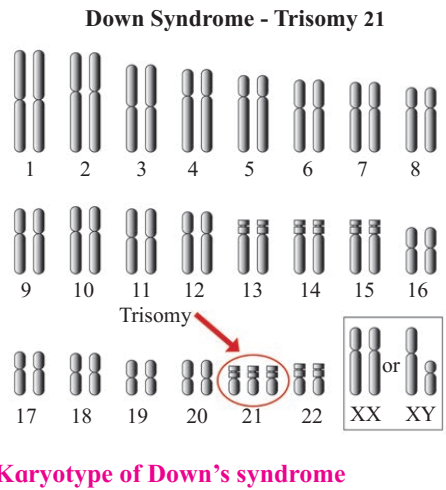
These individuals will have 47 chromosomes instead of the normal number 46.
21st Trisomy occurs due to non-disjuction or failure of separation of chromosomes (autosomes) during gamete formation.
The incidence of non-disjunction is distinctly higher in mothers who are over 45 years old.
These patients have mild or moderate mental retardation and skeletal development is poor.
Distinct facial features like small head, ears and mouth, face is typically flat and rounded with flat nose, open mouth and protruding tongue, eyes slant up and out with internal epicanthal folds, flat hands and stubby fingers and palm is broad with single palmer crease.
Turner's Syndrome :
(X monosomy / XO females)
It is sex chromosomal disorder caused due to non-disjunction of chromosome during gamete formation.
Individual born with Turner's syndrome has 44 autosomes with XO.
They are phenotypically female.
They have a short stature (height) and webbed neck, lower posterior hair line, broad shield-shaped chest, poorly developed ovaries and breast, and low intelligence.
Klinefelter's syndrome (XXY males) :
It is chromosomal disorder caused due to extra X chromosome in males. Thus genotype of individuals is 44 + XXY.
They are described as feminized males.
Extra chromosome is a result of non-disjunction of X-chromosome during meiosis.
Individual is male and has over all masculine development.
Voice pitch is harsh and have under developed testis.
They are tall with long arms, feminine development(development of breast i.e. Gynaecomastia) and no spermatogenesis, therefore, individuals are sterile.
