3.4 Back Cross and Test Cross :
a. Back cross :
The F1 individuals obtained in a cross are usually selfed to get the F2 progeny. They can also be crossed with one of the two parents from which they were derived (either recessive or dominant). Such a cross is known as back cross.
b. Test cross :
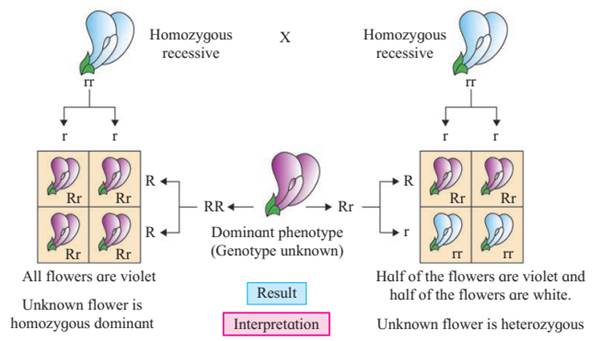
The cross of F1 hybrid with the homozygous recessive parent is known as a test cross. It is used to test whether an individual is homozygous (pure) or heterozygous(hybrid). Test cross is easy, simple, repeatable and predictable.
Test cross can be used to find out genotype of any plant with dominant expression. But it is not known whether it is homozygous (pure) or heterozygous for that trait.
For example, A pea plant having violet (purple) flowers is crossed with a pea plant with white flowers. If all flowers produced are violet, we can conclude that plant is pure or homozygous and if we get violet and white flowers in 1:1 ratio, we can conclude that plant is heterozygous.
Test cross is also used to introduce useful recessive traits in the hybrids of self pollinated plants during rapid crop improvement programs. Following is the graphic representation of test cross. Recessive parent is crossed to find out unknown genotype.