8.1 Tissue :
Anatomy is the study of internal structure of organism. Organs are made up of group of cells.
A group of similar or dissimilar cells having essentially a common function and origin is called as tissue.
Plant tissues are grouped as meristematic tissue and permanent tissue on the basis of its ability to divide.
8.2 Meristematic Tissue :
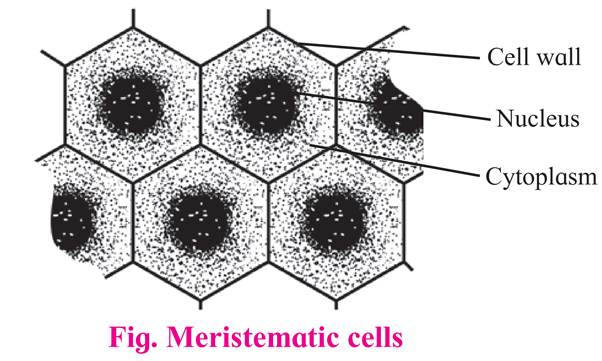
It is a group of young cells. These are living cells with ability to divide in the regions where they are present.
These are polyhedral or isodiametric in shape without intercellular spaces.
Cell wall is thin, elastic, mainly composed of cellulose.
Protoplasm is dense with distinct nucleus at the center and vacuoles if present, are very small.
Cells show high rate of metabolism.
These cells are immature.
A. Classification of Meristem :
Following criteria are used for classification of meristems viz.
1. origin
2. function
3. position
1. Origin :
Primordial meristem or promeristem is also called as embryonic meristem. Usually occupying very minute area at the tip of root and shoot.
Primary meristem originates from the primordial meristem and occurs in the plant body from the beginning, at the root and shoot apices. Cells are dividing and different permanent tissues are produced from primary meristems.
Secondary meristematic tissues develop from living permanent tissues during later stages of plant growth; hence are called as secondary meristems. This tissue occurs in the mature regions of root and shoot of many plants. Secondary meristem is always lateral (to the central axis) in position e.g. fascicular cambium, inter fascicular cambium, cork cambium.
2. Position :
Apical meristem is produced from promeristem and forms growing point of apices of root, shoot and their lateral branches. It brings about increase in length of plant body and called as apical initials.
Shoot apical meristem is terminal in position whereas in root it is subterminal i.e. located behind the root cap.
Intercalary meristematic tissue is present in the top or base area of node. Their activity is mainly seen in monocots. These are short lived.
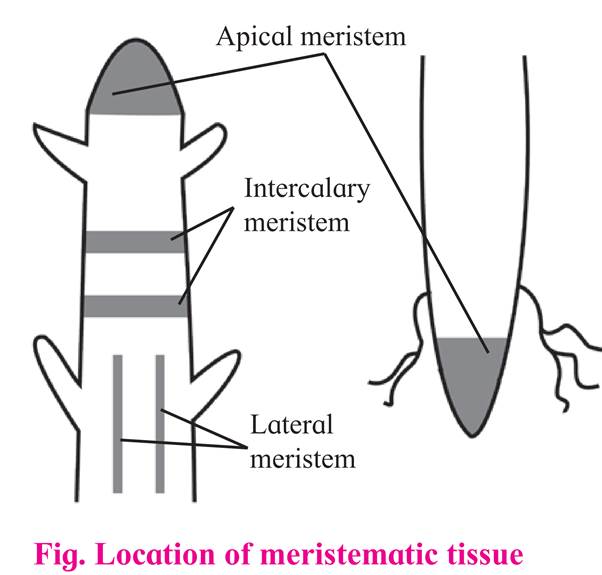
Lateral meristem is present along the sides of central axis of organs. It takes part in increasing girth of stem or root.
eg. intrafascicular cambium. It is found in vascular bundles of gymnosperms and dicot angiosperms.
3. Function :
Young growing region of the plant has Protoderm that forms protective covering like epidermis around the various organs.
Meristem called Procambium is involved in developing primary vascular tissue while the other structures like cortex, endodermis, pericycle, medullary rays, pith are formed from the region of Ground meristem.
These are the three groups of meristem based on function.
