8.4 Tissue Systems :
Plant tissues are derived from meristems and their structure and functions depend on the position.
On the basis of their structure and location, three types of tissue systems are present viz.
1. Epidermal tissue system,
2. Ground tissue system and
3. Vascular tissue system.
A. Epidermal tissue system :
It forms the outer covering of plant body and is derived from protoderm or dermatogen.
The two types of structures are seen in epidermal tissue system viz
1. Epidermis
2. Epidermal appendages.
Epidermis
Epidermis is the outermost protective cell layer made up of compactly arranged cells without intercellular spaces.
Cells show presence of central large vacuole, thin cytoplasm and a nucleus.
The outer side of the epidermis is often covered with a waxy thick layer called the cuticle which prevents the loss of water. It may bear hairs.

Root epidermis has root hairs. These are unicellular elongated and involved in absorption of sap from the soil.
In stem, epidermal hairs are called trichomes. These are generally multicellular, branched or unbranched, stiff or soft or even secretory. These help in preventing water loss due to transpiration.
Stoma
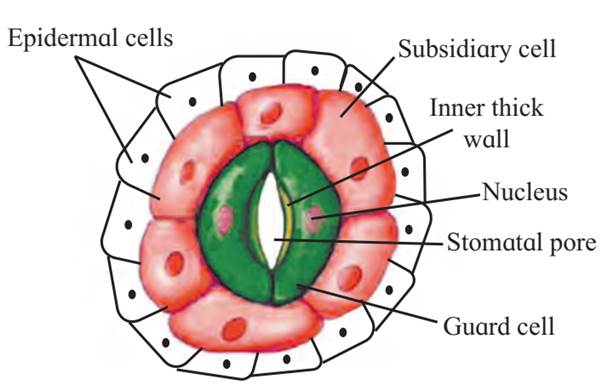
Small gateways in the epidermal cells are called as stoma. Such stoma are controlled or guarded by specially modified cells called guard cells.
These guard cells may be kidney shaped (dicot) or dumbbell shaped (monocot), collectively called as Stomata.
Stoma, guard cells and subsidiary cells form a unit called stomatal apparatus.
Stomata are further covered by subsidiary cells.
Guard cells have few chloroplasts to carry out photosynthesis.
Guard cells change their turgor pressure causing opening and closing of stoma, thus they play a vital role in exchange of gases and water vapour.
B. Ground tissue system :
All the plant tissues excluding epidermal and vascular tissues is ground tissue.
It is made up of simple permanent tissue e.g. parenchyma.
It is present in cortex, pericycle, pith and medullary rays in the primary stem and root.
Collenchyma and sclerenchyma in the hypodermis and chloroplasts containing mesophyll tissue in leaves also constitute ground tissue.
Vascular tissue system :
These are the distinct arches of the complex tissue viz. Xylem and phloem.
On the basis of their arrangement in the plant body these are radial when both the complex tissue are situated separately on separate radii as separate bundle. This is a common feature of roots.
In the stem, the complex tissue is collectively present as neighbours of each other on the same radius in the form where xylem is inside and phloem is outside hence called conjoint, collateral, vascular bundles.
These bundles may be further of open type (secondary growth takes place) containing cambium in between them and closed type if cambium is not present (secondary growth absent). When phloem is present in a vascular bundle on both the sides of xylem and intervening cambium tissue, it is called bicollateral vascular bundle. It is a feature of family Cucurbitaceae.
When one vascular tissue is completely encircling the other, it is called as concentric vascular bundle, this may be
- leptocentric (phloem encircled by xylem) or
- hadrocentric (xylem encircled by phloem).
When one complex tissue is encircling on both the faces of the other it is
- amphicribral (xylem encircled by phloem on both faces) and
- amphivasal (phloem encircled by xylem on both faces).

