8.6 Wood :
During favourable conditions, spring wood (early wood) is formed which has broader xylem bands, lighter colour, tracheids with thin wall and wide lumen, fibres are less in number, low density.
Whereas, during unfavourable season autumn wood (late wood) is formed which has narrow xylem band, darker in colour, lumen is narrow and walls are thick with abundant fibres are present of high density.
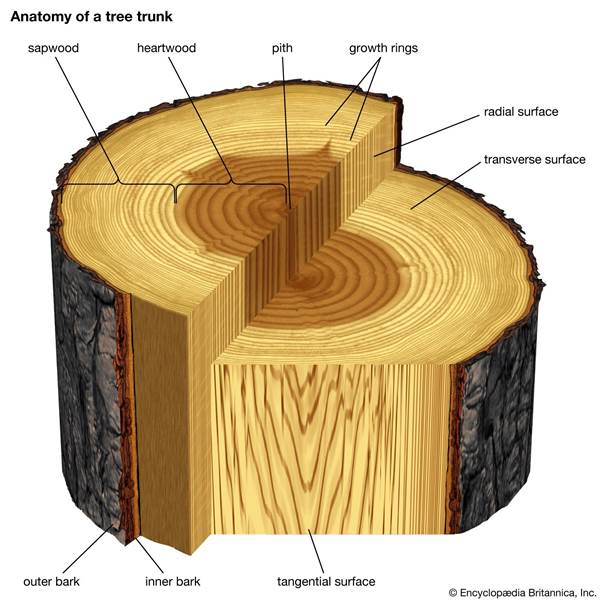
Tracheary elements of heartwood are plugged by in-growth of adjacent parenchyma cells i.e. tyloses. They are filled by oils, gums, resins, tannins called as extractives. Thus inner non-functinal, durable part which is resistant to pathogens is called duramen or heartwood.
Outer light, functional part of secondary xylem, cells are living, no deposition, lighter and less durable, more susceptible to pathogens and involved in conduction of sap is called as sap wood (alburnum).
8.7 Cork cambium and secondary growth:
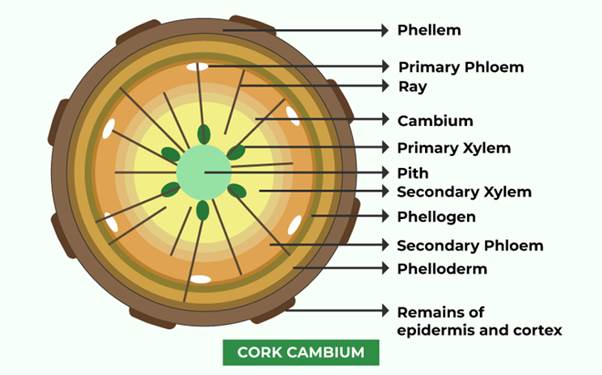
Increase in diameter of stem by secondary growth is mainly due to the activity of vascular cambium present in the outer cortical layer. When epidermis gets ruptured, it becomes necessary to replace these cells by new cells. Phellogen (cork cambium) develops in extrastelar region of stem.
The outer cortical cells of cortex become meristematic and produce a layer of thin walled, rectangular cells. These cells cut off new cells on both sides. The cells produced on outer side develop phellem (cork) where as on the inner side produce phelloderm (secondary cortex).
The cork is impervious in nature and does not allow entry of water due to suberized walls.
Secondary cortex is parenchymatous in nature.
Phellogen, phellem and phelloderm constitute periderm.
Activity of cork cambium develops a pressure on the other cells and these cells die.
Bark is non-technical term refering to all cell types found external to vascular cambium including secondary phloem.
Bark of early season is soft and of the late season is hard.
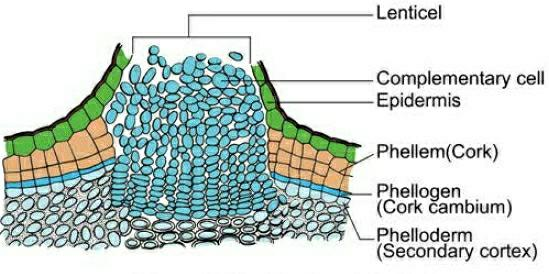
Lenticles are aerating pores present (as raised scars) on the surface of bark. These are portions of periderm, where phellogen activity is more, lenticles are means for gaseous and water vapour exchange.
Monocot stems lack cambium hence secondary growth does not take place. But accessory cambium development in plants like, Dracena, Agave, Palms and root of sweet potato show presence of secondary growth. This is called as anomalous secondary growth.
