B. Bryophyta
(Bryon : moss ; phyton : plant)
|
Feature |
Details |
|
Habitat |
Mostly terrestrial; found in moist, shady places |
|
Water Requirement |
Critically dependent on water for fertilization and life cycle completion |
|
Common Name |
"Amphibious Plants" |
|
Diversity |
~960 genera and ~25,000 species |
|
Root-like Structures |
Rhizoids (unicellular in liverworts; multicellular in mosses) |
|
Rhizoid Functions |
Absorb water and minerals; help fixation on substratum |
|
Life Cycle |
Shows sporophytic and gametophytic stages |
|
Vegetative Body |
Thalloid or leafy (represents gametophytic generation) |
|
Spore Producer |
Capsule (represents sporophytic generation) |
Bryophytes are divided into two groups :
liverworts and mosses.
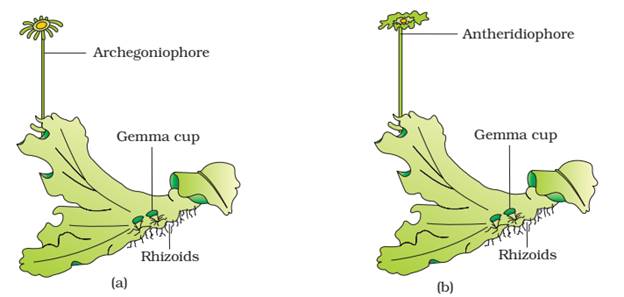
a. Liverworts (Hepaticeae) ;
These are lower members of Bryophyta.
These are primitive group of Bryophytes.
Gametophyte possesses flat plant body called thallus.
The thallus is green, dorsiventral, prostrate with unicellular rhizoids.
e.g. Riccia, Marchantia.
Hornworts (Anthocerotae) -
These member possess flattened thallus. The thallus produces homy structures which are called sporophytes hence the name hornworts.
e.g. Anthoceros.
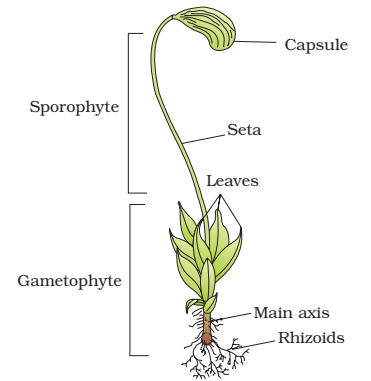
b. Mosses (Musci) :
These are advanced members of Bryophyta which possess erect plant body Gametophytic phase of the life cycle includes two stages namely;
1. Protonema stage
2. leafy stage.
The protonema is prostrate green, branched and filamentous (it is also called juvenile gametophyte). It bears many buds.
Leafy stage is produced from each bud. Thus protonema helps in the vegetative propagation.
The leafy stage has erect, slender stem like (Cauloid) main axis bearing spiral leaf like structures (Phylloid). It is fixed in soil by multicellular branched rhizoids. This stage bears sex organs.
Vegetative reproduction takes place by fragmentation and budding in secondary protonema.
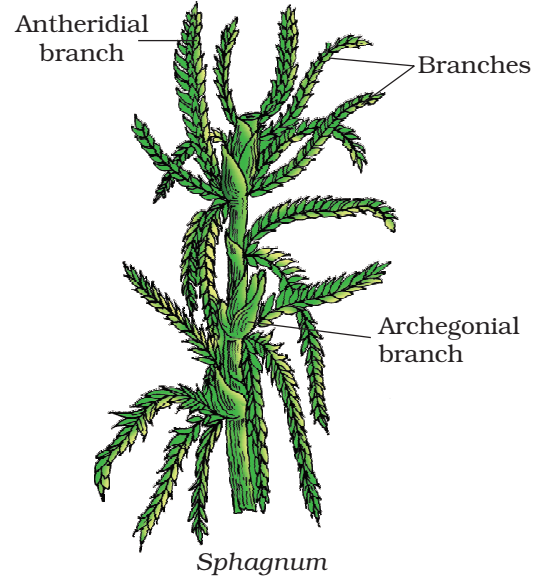
e.g. Funaria, Polytrichum, Sphagnum, etc.
Economic importance -
Some mosses provide food for herbivorous mammals, birds, etc.
Species of Sphagnum, a moss; provides peat used as fuel.
Mosses are also used as packing material for transport of living materials because they have significant water holding capacity.
Just like lichens, mosses are the first living beings to grow on rocks. They decompose rocks to form soil and make them suitable for growth of higher plants.
Dense layers of mosses help in prevention of soil erosion, thus act as soil binders.
