B. Angiospermae
- Most advanced group of flowering plants
- Seeds enclosed within fruit (ovary)
- Highly evolved plants, primarily adapted to terrestrial habitats
- Vast diversity in size, shape, and form
General Characteristics:
|
Feature |
Details |
|
Reproduction |
Sexual, with flowers and fruits |
|
Seed Enclosure |
Seeds enclosed within ovary (fruit) |
|
Plant Body |
Sporophyte (diploid, dominant, autotrophic, independent) |
|
Gametophytes |
Haploid, reduced, parasitic, concealed in sporophyte |
|
Alternation |
Heteromorphic (different forms of generations) |
|
Diversity |
Enormous variation in size, form, and habitat |
|
Reproduction Mechanism |
Double fertilization (unique to angiosperms) |
Size Range:
|
Species |
Size |
|
Wolffia |
Smallest angiosperm (~1 mm) |
|
Eucalyptus |
Tallest angiosperm (>100 meters) |
Reproductive Features:
-
Heterosporous: Produce two types of spores
- Microspores (Pollens): Formed in microsporangia (anthers) within microsporophylls (stamens)
-
Megaspores: Formed in megasporangia (ovules) borne on megasporophyll (carpel)
Floral Structure:
|
Whorl |
Components |
|
Essential Whorls |
Androecium (stamens - microsporophylls); Gynoecium (carpels - megasporophylls) |
|
Accessory Whorls |
Calyx (sepals); Corolla (petals) |
All whorls together form the flower
a. MONOCOTYLEDONAE (Monocots)
Characteristics:
|
Feature |
Monocot Characteristics |
|
Cotyledons |
Single cotyledon in embryo |
|
Root System |
Adventitious (not from tap root) |
|
Stem Branching |
Rarely branched |
|
Leaf Base |
Sheathing |
|
Venation |
Parallel venation |
|
Flower Parts |
Generally trimerous (multiples of 3) |
|
Vascular Bundles |
Conjoint, collateral, closed type |
|
Secondary Growth |
Absent (except few plants) |
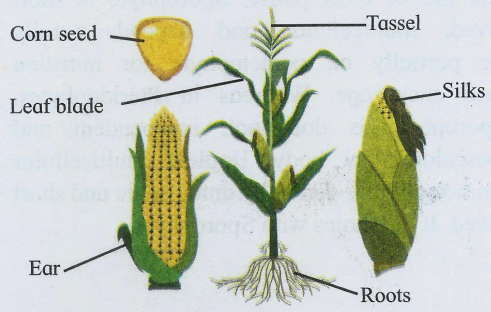
Examples: Zea mays (Maize), Sorghum vulgare (Jowar), Grass, Tulsi
b. DICOTYLEDONAE (Dicots)
Characteristics:
|
Feature |
Dicot Characteristics |
|
Cotyledons |
Two cotyledons in embryo |
|
Root System |
Tap root system (from single primary root) |
|
Stem Branching |
Branched |
|
Leaf Base |
Not sheathing |
|
Venation |
Reticulate venation (net-like) |
|
Flower Parts |
Tetra- or pentamerous (multiples of 4 or 5) |
|
Vascular Bundles |
Conjoint, collateral, open type |
|
Cambium |
Present between xylem and phloem |
|
Secondary Growth |
Commonly found |
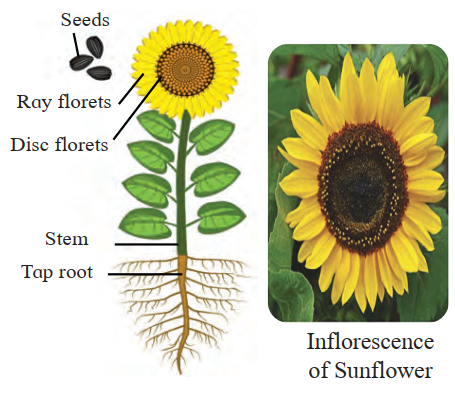
Examples: Helianthus annuus (Sunflower), Hibiscus rosa-sinensis (China rose), Pea, Peepal
Comparative Summary - Monocots vs Dicots:
|
Character |
Monocotyledonae |
Dicotyledonae |
|
Cotyledons |
1 |
2 |
|
Roots |
Adventitious (fibrous) |
Tap root |
|
Stem |
Non-branched |
Branched |
|
Leaf Venation |
Parallel |
Reticulate |
|
Flower Symmetry |
Trimerous (3s) |
Tetramerous/Pentamerous (4s/5s) |
|
Vascular Bundles |
Conjoint, collateral, closed |
Conjoint, collateral, open |
|
Cambium |
Absent |
Present |
|
Secondary Growth |
Absent |
Present |
|
Girth Increase |
NO |
YES |
1. What are the salient features of Angiosperms?
2. What is double fertilization ?
3. Explain in brief two classes of Angiosperms? Draw and label one example of each class.
4. Give general characters of Gymnosperms and Angiosperms.
5. Distinguish between Dicotyledonae and Monocotyledonae.
6. Why do Dicots show secondary growth while Monocots don't?
