3.4 Plant life cycle and alternation of generations:
Life cycle of a plant includes two phases or distinct generations namely sporophyte (diploid : 2n) and gametophyte (haploid : n).
Some special diploid cells of sporophyte divide by meiosis to produce haploid cells.
These haploid cells divide mitotically to give rise to gametophyte.
The gametophyte produces male and female gametes which fuse during fertilization to produce diploid zygote.
It divides by mitosis to form diploid sporophyte. The sporophytic and gametophytic generations generally occur alternately in the life cycle of a plant. This phenomenon is called alternation of generations.
Distinct alternation of these two generations is observed in Bryophytes and Pteridophytes.
In Gymnosperms and Angiosperms, gametophyte is much reduced and exists within sporophyte.
Based upon the nature of dominant phase in life cycle, it is called haplontic, diplontic or haplodiplontic life cycles.
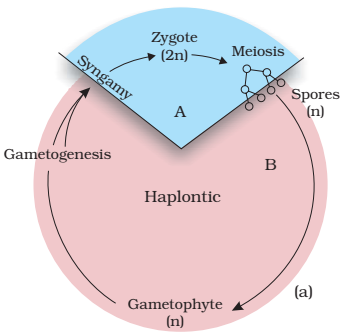
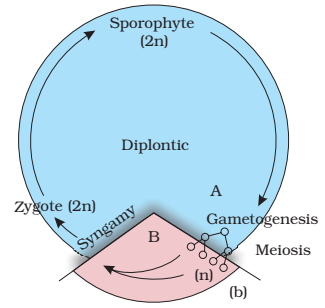
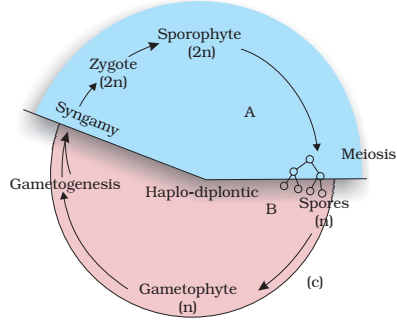
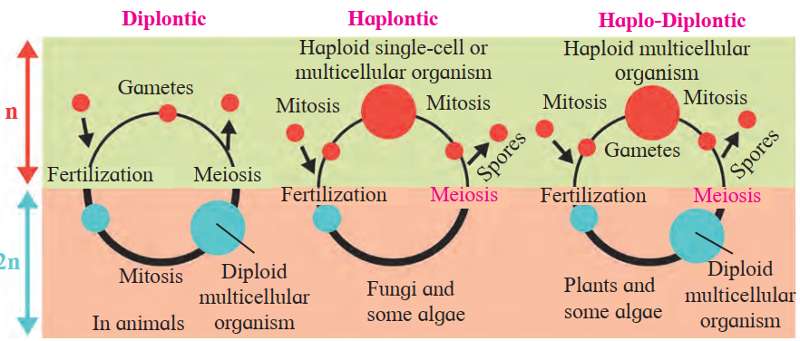
Life cycle patterns : (a) Haplontic (b) Diplontic (c) Haplo-diplontic
In Bryophytes haploid gametophyte is dominant. It is photosynthetic, independent thalloid or erect phase. Sporophyte is short lived, multicellular and depends totally or partially on gametophyte for nutrition and anchorage.
Whereas in Pteridophytes, sporophyte is dominant, independent and vascular plant body. Haploid multicellular gametophyte is generally autotrophic and short lived. It alternates with Sporophyte.
1. What is alternation of generations?

2. Which phase is dominant in the life cycle of Bryophyta and Pteridophyta ?

Types of Life Cycles Based on Dominant Phase:
1. HAPLONTIC LIFE CYCLE
Characteristics:
- Mitosis occurs
in haploid cells
- Result:Single haploid cells or multicellular haploid organisms
- Gamete Formation:
Through mitosis
- Zygote:Only diploid cell in entire life cycle
- Meiosis:
Zygote undergoes meiosis
- Dominant Phase:Haploid gametophyte
Examples:Some algae and fungi
Diagram Feature:
- Haploid multicellular organism → Gametes (mitosis) → Zygote (2n) → Spores (meiosis) → Return to haploid
2. DIPLONTIC LIFE CYCLE Characteristics:
- Mitotic divisions
occur only in diploid cells
- Gametes:Formed through meiosis (haploid)
- Zygote:
Divides mitotically
- Result:Multicellular diploid organisms or many diploid single cells
- Dominant Phase:
Diploid sporophyte
Animals Diagram Feature:
- Diploid multicellular organism → Gametes (meiosis) → Zygote (2n) → Organism (mitosis) → Return to diploid
3. HAPLO-DIPLONTIC LIFE CYCLE
3. HAPLO-DIPLONTIC LIFE CYCLE
Characteristics:
- Mitosis occursin both diploid AND haploid cells
- Two multicellular phases:
- Gametophyte:
Multicellular and haploid
- Sporophyte:Multicellular and diploid
- Both phases independent
to varying degrees
- Both alternates regularly
Land plants and many algae Diagram Feature:
- Diploid multicellular organism ↔ Haploid multicellular organism
- Continuous alternation through meiosis and fertilization
Dominance Patterns in Different Plant Groups:
Dominance Patterns in Different Plant Groups:
In Bryophytes:
- Gametophyte is dominant(haploid)
- Photosynthetic, independent, thalloid or erect
- Sporophyte: Short-lived, multicellular, dependent on gametophyte for nutrition and anchorage
In Pteridophytes:
- Sporophyte is dominant(diploid)
- Independent, vascular plant body
- Gametophyte: Haploid, multicellular, independent, generally autotrophic, short-lived, non-vascular
In Gymnosperms & Angiosperms:
- Gametophyte much reduced
- Gametophyte exists within sporophyte
- Sporophyte is highly developed and dominant
In Algae:
-
Variable: Based on nature of dominant phase
- Can be haplontic, diplontic, or haplo-diplontic
