3.3 Salient features of major plant groups under Phanerogams
A. Gymnospermae
(Gymnos : naked, sperma : seed)
- ~70 genera and 1,000 living species worldwide
- In India: 16 genera and 53 species
- Most ancient seed-producing plants
General Characteristics:
|
Feature |
Details |
|
Form |
Evergreen shrubs or woody trees |
|
Seed Type |
Naked seeds (not enclosed in fruit) |
|
Vascular Tissue |
Xylem: tracheids; Phloem: sieve cells |
|
Plant Body |
Sporophyte (diploid, dominant) |
|
Differentiation |
Into root, stem, and leaves |
|
Root Type |
Tap root system |
|
Root Association |
Symbiotic; some show mycorrhizal associations |
|
Secondary Growth |
Present (due to cambium) |
|
Stem Structure |
Mostly erect, aerial, solid, cylindrical; branched or unbranched |
|
Leaf Structure |
Dimorphic (two types) |
|
Spore Production |
By microsporophyll (male) and megasporophyll (female) |
Leaf Dimorphism:
|
Leaf Type |
Characteristics |
|
Foliage Leaves |
Green, simple, needle-like or pinnately compound |
|
Scale Leaves |
Small, membranous, brown |
Root Adaptations:
|
Gymnosperm |
Root Adaptation |
Associated Organism |
|
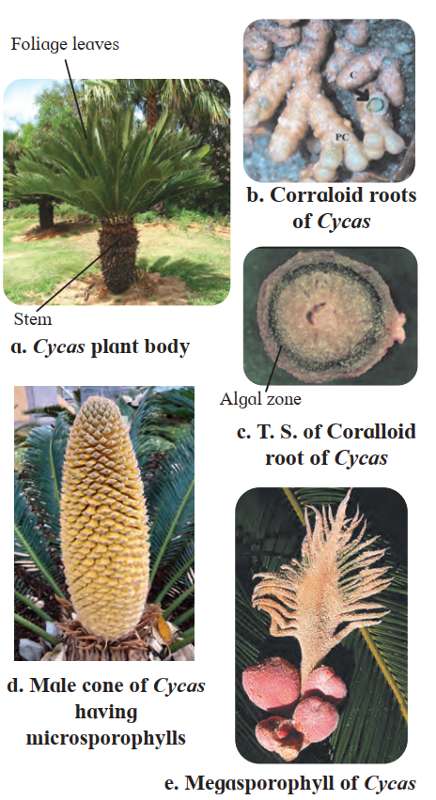
Cycas |
Coralloid roots |
Blue-green algae (cyanobacteria) |
|
Pinus |
Regular roots |
Endophytic fungi (mycorrhizae) |
Size Variation in Gymnosperms:
|
Species |
Characteristic |
Measurement |
|
Sequoia sempervirens |
Tallest gymnosperm (coast redwood) |
~366 feet |
|
Taxodium mucronatum |
Largest girth |
~125 feet |
|
Zamia pygmaea |
Smallest gymnosperm |
~25 cm |
Living Fossils:
- Ginkgo biloba: Found in living form as well as fossil form; fossil forms more abundant than living forms
Economic Importance:
- Cycas: Grown as ornamental plant
- Pinus:
- Pine wood (timber)
- Turpentine oil
- Pine resin