4.5 Protein synthesis :
Proteins are very important biomolecules. They serve as structural components, enzymes and hormones. The cell needs to synsthesize new protein molecules.
The process of protein synthesis includes transcription and translation.
The process of copying of genetic information from one (template) strand of DNA into a single stranded RNA transcript, is termed as transcription.
During this process, synthesis of complementary strand of RNA takes place (Except that the Adenine nitrogen base pairs with the Uracil base instead of Thymine).
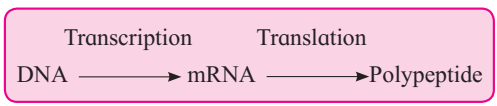
Central Dogma :
Double stranded DNA molecule gives rise to mRNA which acts as a messenger to programme the synthesis of a polypeptide chain (protein).
This type of unidirectional flow of information from DNA to RNA to protein/ proteins is referred as central dogma of molecular biology.
It was postulated by F.H.C. Crick in 1958.
The present concept of central dogma in retroviruses or riboviruses is given by Temin (1970) and Baltimore (1970):
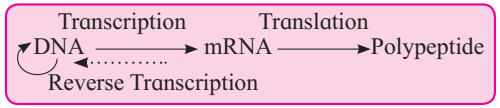
Accordingly enzyme RNA dependent DNA polymerase, synthesizes DNA from RNA.
