Sexual Reproduction
It is also called as Amphimixis. It origination of word is amphi =both and mixis= mixing.
It involves mixing or fusion of genetic material of male and female gametes.
Angiosperms are commonly called flowering plants because they produce a prominent, highly specialized organ called flower for sexual reproduction.
Formation of fruits and seeds are the further stages of sexual reproduction.
The life cycle of sexually reproducing plants shows alternate occurrence of diploid phase called sporophyte and haploid phase called gametophyte.
In Angiosperms, the plant itself is diploid, highly differentiated sporophyte while the haploid male and female gametophytes are much reduced and microscopic.
Diploid zygote (2n) is the initial stage of the sporophyte while haploid microspores (n) and megaspores (n) are the initial cells of male and female gametophytes respectively.
Flower Structure
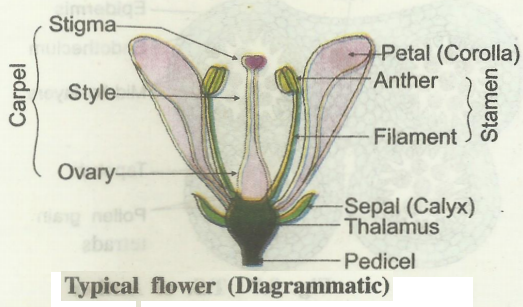
Flower is a site of sexual reproduction. It can be deined as highly evolved (modified) shoot, specially designed for sexual reproduction.
Thalamus of the flower is a shoot with condensed intemodes. At nodes floral whorls (leaf like sepals, petals, stamens and carpels) are produced.
Stamens and carpels are the male and female reproductive whorls respectively.
Anther of stamen and ovule of carpel produce microspores (commonly called pollen grains) and megaspores which develop into male and female gametophytes respectively.
After pollination and fertilization, formation of fruits and seeds takes place and from seed new plant is produced.
Thus, process of sexual reproduction in Angiosperms involves;
- microsporogenesis
- formation of microspores (pollen grains),
- megasporogenesis i.e. formation of megaspores,
- development of male and female gametophytes,
- pollination,
- fertilization and formation of fruits and seeds.
It is, therefore important to study the structure of anther and ovule.
