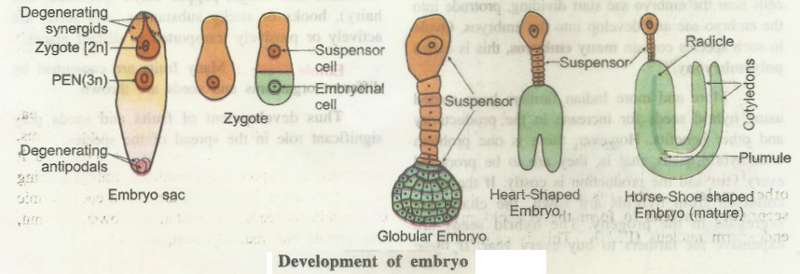
Development of Embryo:
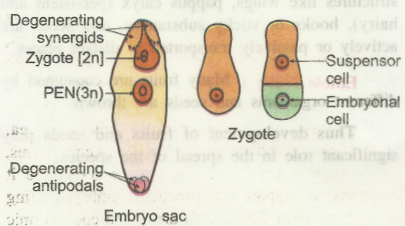
The zygote forms a wall around it and is converted into oospore.
The oospore divides transversely to form a large basal cell (or suspenser cell) towards the micropyle and a small apical cell (or embryonal cell) towards the inteior of embryo sac.
From this 2 celled stage, until the formation of organs the embryo is commonly called pro-embryo.
The basal cell divides transversely to form a row of cells called suspensor.
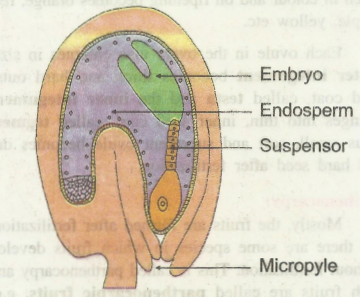
The suspensor pushes the developing embryo deeper in the endosperm for its proper nutrition.
The apical cell of the 2- celled pro-embryo undergoes a transverse and two vertical divisions at right angles to each
other to form an octant stage. The eight cells of octant pro-embryo undergo many divisions to form a spherical mass of cells.
Gradually this mass becomes heart-shaped and then horse-shoe shaped.
Finally it gets differentiated to form an embryonal axis with plumule, radicle and two cotyledons in dicots and a single cotyledon in monocots