Androecium:
Androecium is male reproductive whorl of flower and is made up of one or more stamens.
A stamen represents a modified (evolved) male reproductive leaf - microsporophyll which produces microspores.
When the stamens are free from each other, the androecium is said to be polyandrous.
When the stamens are united to the petals they are described as epipetalous, (e.g. Datura)
Each stamen consists of three parts,
1. filament,
2. anther and
3. connective.
Filament is stalk of stamen that bears anther at its tip.
It raises the anther for better dispersal of pollen grains.
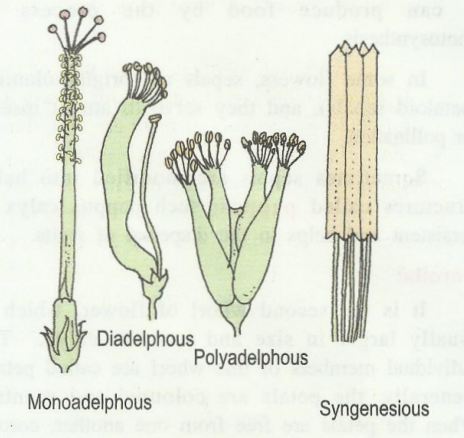
When stamens are united by their filaments and anthers are free, it is known as adelphy.
Androecium can be
monoadelphous (e.g.Hibuscus),
diadelphous (e.g. Pea) or
polyadelphous (e.g. Lemon)
The filaments are united to form single bundle (staminal tube) or two bundles or many bundles.
Anther is the upper swollen fertile part of stamen, usually having two lobes.
Each lobe has two chambers or locules called pollen sacs or microsporangia within which pollen grains (microspores) are produced.
A two-lobed anther is called dithecous anther.
An anther with a single lobe is called monothecous anther.
Pollen grains are male reproductive units or male spores.
When anthers are united and filaments are free it is known as Syngeny.
In sunflower syngenecious condition is observed.
Connective is in continuation with the filament.
It is a midrib-like, sterile structure between the two fertile lobes of the anther connecting them together-lengthwise.
