9.3 Study of Some Important Families
Families are groups of plants havingvery distinguished common characters.
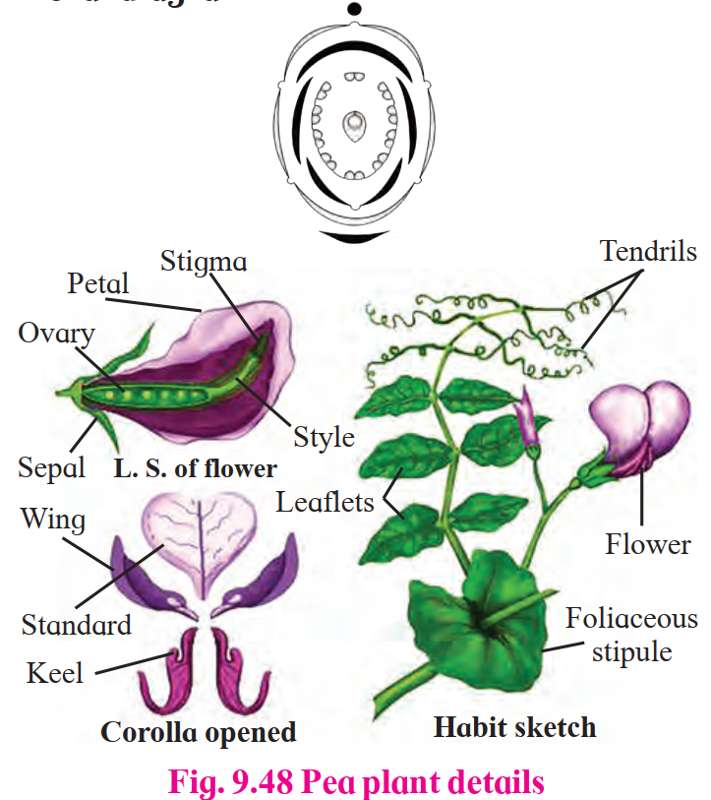
1. Fabaceae
Habit
Trees, shrubs, or herbs (Pea plant belongs here)
Root
- Shows root nodules
-
Pea is an erect climber
Leaf
- Pinnately compound
- Alternate phyllotaxy
Inflorescence
- Racemose type (raceme)
Flower
- Bisexual and zygomorphic
Calyx
- Five fused sepals (gamosepalous)
- Imbricate aestivation
Corolla
- Five free petals (polypetalous)
- Vexillary aestivation:
- Vexillum: Outermost
- Two wings: Lateral petals
- Two fused petals: Keel
Androecium
- Ten stamens
-
Arrangement: Diadelphous[(9)+1]
- 9 stamens united by filaments
- 1 stamen free
Gynoecium
- Monocarpellary
- Unilocular ovary (superior)
- Marginal placenta
Fruit
- Legume type
Seed
- Non-endospermic
Floral Formula
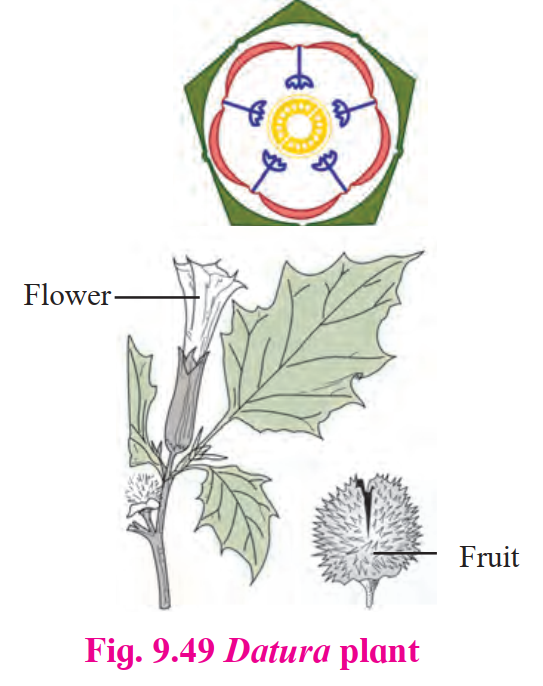
2. Solanaceae
Habit
Herbs, shrubs, or small trees (Daturaplant belongs here)
Root
- Tap root system
Stem
- Erect, woody, branched
- Underground tuber in potato
Leaf
- Simple
- Alternate phyllotaxy
- Reticulate venation
Inflorescence
- Cymose type (solitary)
Flower
- Solitary, bisexual, and actinomorphic
Calyx
- Five fused sepals (gamosepalous)
- Valvate aestivation
- Persistent
Corolla
- Five fused petals (gamopetalous)
- Contorted aestivation
Androecium
- Five stamens
- Free but
epipetalous(adhesion with petals)
Gynoecium
- Bicarpellary and syncarpous
- Bilocular ovary (superior)
- Many ovules in axile placentation
- Arranged on swollen placenta
Fruit
- Berry or capsule type
Seed
- Endospermic
Floral Formula