F. Fruit
Angiosperms produce fruit after fertilization from the ovary.
Types
Parthenocarpic Fruits
-
Fruits produced from ovary without fertilization
- Example: Seedless grapes
True Fruit
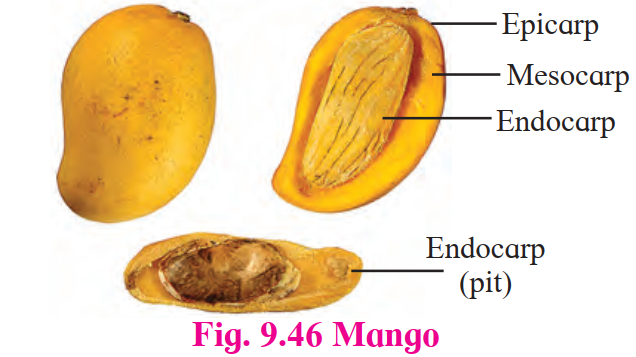
-
Develops only from ovary
- Example: Mango
False Fruit (Pseudocarp)
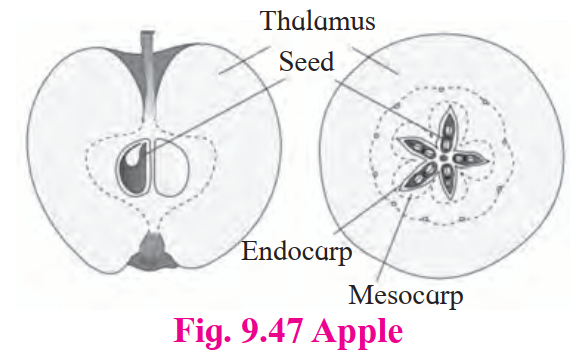
-
Develops from other floral parts than ovary
- Example: Apple
Structure of a True Fruit
Components:
- Protective wall (Pericarp): Contains seeds
In Fleshy Fruits, pericarp is further divided:
- Epicarp: Outer layer
- Mesocarp: Middle layer
- Endocarp: Inner layer
- Example: Mango

Types of Fruits
Simple Fruits
-
Develop from one ovary of one flower

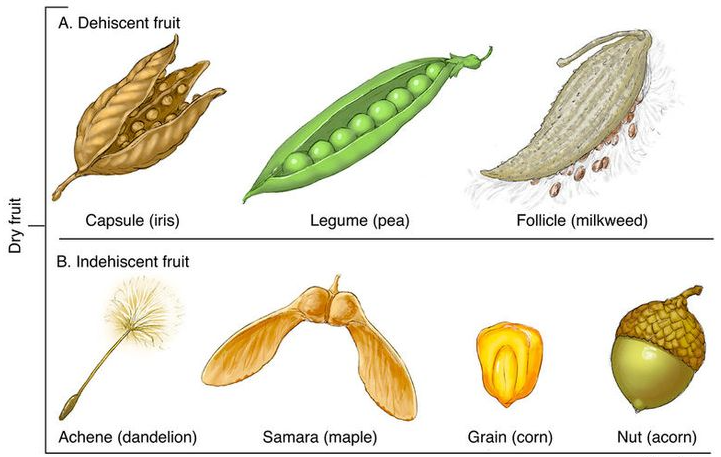
Dry Fruits
- Thin pericarp
- Dehiscent: Breaks open at maturity (e.g., Capsule, Legume)
- Indehiscent: Does not break open (e.g., Achene, Caryopsis, Cypsela)
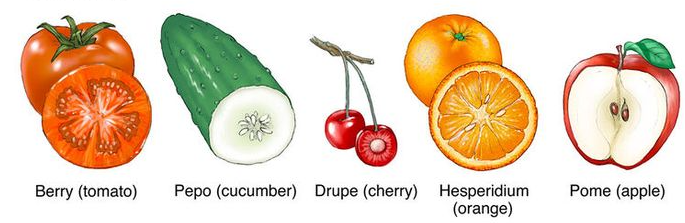
Fleshy Fruits
- Thick pericarp
- Examples: Berry, drupe
Aggregate Fruits
-
Develop from many ovaries of apocarpous gynoecium
- Also called collection/Etario
- Example: Etario of achenes = Strawberry
Composite Fruits
-
Develop from one whole inflorescence
- Examples:
- Syconus: Fig
- Sorosis: Pineapple

Fruit Types and Structure
|
Category of Fruit |
Type of Fruit |
Structure/Definition |
Characteristics |
Examples |
|
Parthenocarpic Fruits |
Parthenocarpic Fruits |
Fruits produced from ovary without fertilization |
No seeds present; seedless variety |
Seedless grapes |
|
True Fruit |
True Fruit |
Develops only from ovary after fertilization |
Contains seeds; ovary wall becomes pericarp with three layers (Epicarp - outer, Mesocarp - middle, Endocarp - inner) |
Mango |
|
False Fruit |
False Fruit (Pseudocarp) |
Develops from other floral parts than ovary |
Includes tissues from receptacle, calyx, or other floral parts |
Apple |
|
SIMPLE FRUITS |
Dry Fruits - Dehiscent |
Develop from one ovary of one flower; thin pericarp; breaks open at maturity |
Pericarp splits to release seeds; fruit ruptures naturally at maturity |
Capsule, Legume |
|
Dry Fruits - Indehiscent |
Develop from one ovary of one flower; thin pericarp; does not break open |
Pericarp remains intact at maturity; seeds not released from fruit |
Achene, Caryopsis, Cypsela |
|
|
Fleshy Fruits |
Develop from one ovary of one flower; thick pericarp with three distinct layers (Epicarp - outer layer, Mesocarp - middle layer, Endocarp - inner layer) |
Soft, succulent, fleshy tissue; pericarp well-developed; edible |
Berry, Drupe |
|
|
AGGREGATE FRUITS |
Aggregate Fruits (Etario) |
Develop from many ovaries of apocarpous gynoecium; also called collection or Etario |
Multiple small fruits (fruitlets) from one flower; clustered together; appear as one unit |
Etario of achenes = Strawberry |
|
COMPOSITE FRUITS |
Composite Fruits - Syconus |
Develop from one whole inflorescence |
Entire inflorescence becomes a single fruit structure; multiple flowers fuse into one fruit body |
Fig |
|
Composite Fruits - Sorosis |
Develop from one whole inflorescence |
Entire inflorescence becomes a single fruit structure; multiple flowers fuse; usually large and compound |
Pineapple |
