Fruit:
Formation of fruit is one of the important characters of Angiosperms.
Usually after successful fertilization an ovary develops to form a fruit.
Parthenocarpy
There are some plants in which fruits are developed even without fertilization.
Such fruits are called parthenocarpic fruits and the phenomenon is known as parthenocarpy.
Such fruits are seedless e.g. grapes, banana, etc.
Fruit - Continued
A fruit is defined as the metamorphosed or a ripened ovary without or with one or more seeds.
When a fruit is developed exclusively from the ovary of a flower, it is called a true fruit, e.g. mango.
Sometimes, other floral parts, like thalamus, or receptacle may develop as a part of the fruit, such fruits are called false fruits or pseudocarps.
For example
in apple and pear the thalamus grows around the ovary and becomes fleshy to form the main edible part of the fruit.
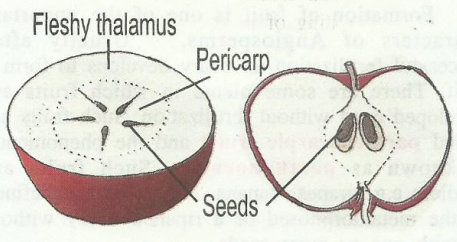
Parts of a typical fruit:
A fruit mainly consist of two parts -
- Pericarp or fruit wall
- Seed(s).
Pericarp-
It is the wall of a fruit, which is developed from ovary wall.
In some plants the pericarp is differentiated into three parts, epi, meso and endocarp.
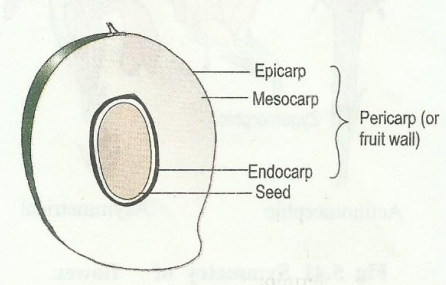
Epicarp -
It is the outer part of the fruit wall, which forms the skin or protective covering of the fruit.
Mesocarp -
It is the middle part of the fruit wall, which forms the major pulpy or juicy part of a fruit as in Mango.
Endocarp -
It is the inner part of the fruit wall, which may be thin and membranous as in
orange or hard and stony as in mango, plum and coconut.
In some plants, pericarp is single, not differentiated into such parts, e.g. Pea, Beans, etc.
